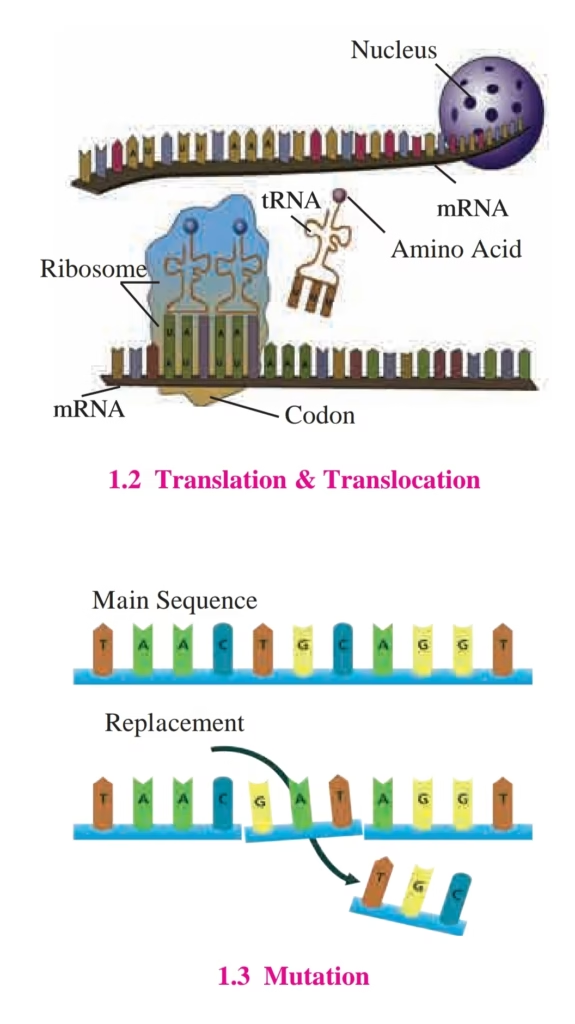
1. Which scientist is known as the pioneer of modern genetics?
a) Charles Darwin
b) Johann Gregor Mendel
c) Hugo de Vries
d) Walter Sutton
Answer:
b) Johann Gregor Mendel
2. What is the process of transferring physical and mental characteristics from parents to offspring called?
a) Mutation
b) Evolution
c) Heredity
d) Adaptation
Answer:
c) Heredity
3. In 1961, which model did François Jacob and Jacques Monod propose?
a) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
b) Process of protein synthesis in bacteria
c) Structure of DNA
d) Natural Selection
Answer:
b) Process of protein synthesis in bacteria
4. What are the building blocks of DNA?
a) Amino acids
b) Nucleotides
c) Proteins
d) Lipids
Answer:
b) Nucleotides
5. Which process involves RNA synthesis from DNA?
a) Translation
b) Translocation
c) Transcription
d) Mutation
Answer:
c) Transcription
6. Who proposed the mutational theory in 1901?
a) Hugo de Vries
b) Walter Sutton
c) François Jacob
d) Charles Darwin
Answer:
a) Hugo de Vries
7. What type of RNA carries the code from DNA to synthesize proteins?
a) mRNA
b) tRNA
c) rRNA
d) snRNA
Answer:
a) mRNA
8. What is the primary role of tRNA during protein synthesis?
a) Synthesizing proteins
b) Carrying amino acids to ribosomes
c) Transcribing DNA
d) Splitting peptide bonds
Answer:
b) Carrying amino acids to ribosomes
9. The sequence of nucleotides in RNA is complementary to which strand?
a) tRNA strand
b) mRNA strand
c) DNA template strand
d) Peptide chain
Answer:
c) DNA template strand
10. What is the term for sudden changes in genes?
a) Speciation
b) Mutation
c) Evolution
d) Natural Selection
Answer:
b) Mutation
11. What replaces thymine in RNA molecules?
a) Uracil
b) Cytosine
c) Adenine
d) Guanine
Answer:
a) Uracil
12. What is the term for the triplet sequence of nucleotides in mRNA?
a) Gene
b) Codon
c) Anticodon
d) Chromosome
Answer:
b) Codon
13. Who discovered the triplet codons for amino acids?
a) Har Gobind Khorana
b) Hugo de Vries
c) François Jacob
d) Gregor Mendel
Answer:
a) Har Gobind Khorana
14. Which organelle is responsible for protein synthesis in cells?
a) Nucleus
b) Ribosome
c) Mitochondria
d) Golgi apparatus
Answer:
b) Ribosome
15. What is the name of the process in which mRNA is decoded to form proteins?
a) Translation
b) Translocation
c) Replication
d) Transcription
Answer:
a) Translation
16. What is the function of rRNA in protein synthesis?
a) Stores genetic information
b) Provides energy for protein synthesis
c) Bonds amino acids together
d) Carries genetic code
Answer:
c) Bonds amino acids together
17. Which genetic disorder is caused by a mutation affecting hemoglobin?
a) Sickle cell anemia
b) Down syndrome
c) Hemophilia
d) Cystic fibrosis
Answer:
a) Sickle cell anemia
18. What evidence supports Darwin’s theory of natural selection?
a) Fossils
b) Mutations
c) Genetic engineering
d) Cloning
Answer:
a) Fossils
19. What is the term for the formation of new species through evolution?
a) Speciation
b) Mutation
c) Adaptation
d) Translocation
Answer:
a) Speciation
20. What is the importance of mutations in evolution?
a) Prevents species extinction
b) Introduces genetic variation
c) Reduces diversity in a population
d) Ensures uniformity in traits
Answer:
b) Introduces genetic variation
21. Who proposed the theory of natural selection?
a) Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
b) Charles Darwin
c) Alfred Wallace
d) Hugo de Vries
Answer:
b) Charles Darwin
22. What was the title of Darwin’s book on evolution?
a) The Descent of Man
b) Origin of Species
c) Evolution of Life
d) Natural Selection
Answer:
b) Origin of Species
23. What did Darwin mean by ‘survival of the fittest’?
a) Strongest organisms always survive
b) Adapted organisms survive and reproduce
c) Largest organisms dominate ecosystems
d) Organisms with fewer predators survive
Answer:
b) Adapted organisms survive and reproduce
24. Which organ in humans is considered vestigial?
a) Appendix
b) Liver
c) Heart
d) Pancreas
Answer:
a) Appendix
25. What is the purpose of the carbon dating method?
a) Determine the structure of fossils
b) Measure the age of fossils
c) Identify genetic mutations
d) Study vestigial organs
Answer:
b) Measure the age of fossils
26. What radioactive isotope is used in carbon dating?
a) Carbon-12
b) Carbon-14
c) Carbon-16
d) Carbon-18
Answer:
b) Carbon-14
27. What is the term for organs that are underdeveloped and non-functional in some species?
a) Vestigial organs
b) Homologous organs
c) Analogous organs
d) Functional organs
Answer:
a) Vestigial organs
28. Which animal is considered a connecting link between amphibians and fishes?
a) Lungfish
b) Platypus
c) Peripatus
d) Salamander
Answer:
a) Lungfish
29. What is the shape of chromosomes during metaphase?
a) X-shaped
b) Linear
c) Circular
d) Helical
Answer:
a) X-shaped
30. Which scientist’s theory proposed the ‘inheritance of acquired characters’?
a) Charles Darwin
b) Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
c) Hugo de Vries
d) Alfred Wallace
Answer:
b) Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
31. What is the concept of ‘use or disuse of organs’ related to?
a) Natural selection
b) Lamarckism
c) Vestigial organs
d) Speciation
Answer:
b) Lamarckism
32. Which example did Lamarck use to explain the theory of inheritance of acquired traits?
a) Development of gills in fish
b) Long neck of giraffes
c) Wings of insects
d) Eyes of birds
Answer:
b) Long neck of giraffes
33. Which type of evidence shows similarity in the embryonic stages of vertebrates?
a) Morphological
b) Anatomical
c) Embryological
d) Palaeontological
Answer:
c) Embryological
34. What is the study of fossils called?
a) Anthropology
b) Archaeology
c) Palaeontology
d) Evolutionary biology
Answer:
c) Palaeontology
35. What is the main function of the appendix in ruminants?
a) Digestion of cellulose
b) Protein synthesis
c) Absorption of nutrients
d) Storage of fats
Answer:
a) Digestion of cellulose
36. Which connecting link demonstrates features of both reptiles and mammals?
a) Duck-billed platypus
b) Peripatus
c) Lungfish
d) Salamander
Answer:
a) Duck-billed platypus
37. What is the term for sudden changes in genetic material?
a) Mutation
b) Transcription
c) Speciation
d) Evolution
Answer:
a) Mutation
38. Which scientist proposed the theory of mutation?
a) Gregor Mendel
b) Hugo de Vries
c) Charles Darwin
d) Alfred Wallace
Answer:
b) Hugo de Vries
39. Which vestigial organ in humans is functional in monkeys?
a) Wisdom teeth
b) Tailbone
c) Ear muscles
d) Appendix
Answer:
c) Ear muscles
40. What is the name of the book published by Charles Darwin?
a) The Evolution of Species
b) Origin of Species
c) The Survival of Fittest
d) Theory of Natural Selection
Answer:
b) Origin of Species
41. What do morphological similarities among species suggest?
a) Similar diet
b) Common ancestry
c) Identical habitats
d) Mutual dependence
Answer:
b) Common ancestry
42. What kind of changes are studied in evolution?
a) Sudden changes in an organism’s lifespan
b) Gradual changes over generations
c) Random changes within a species
d) Seasonal changes in organisms
Answer:
b) Gradual changes over generations
43. Which organ is a vestigial structure in humans but functional in other animals?
a) Tailbone
b) Stomach
c) Lungs
d) Pancreas
Answer:
a) Tailbone
44. What is the key principle in Darwin’s theory of natural selection?
a) Survival of the weakest
b) Survival of the adapted
c) Random mutations
d) Rapid evolution
Answer:
b) Survival of the adapted
45. Which scientist’s theory was disproved due to the non-transferability of acquired traits?
a) Charles Darwin
b) Gregor Mendel
c) Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
d) Hugo de Vries
Answer:
c) Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
46. Which method determines the age of fossils?
a) Evolutionary biology
b) Natural selection
c) Carbon dating
d) Geological mapping
Answer:
c) Carbon dating
47. Who discovered that genes are carried via chromosomes?
a) Gregor Mendel
b) Walter Sutton
c) Hugo de Vries
d) François Jacob
Answer:
b) Walter Sutton
48. What does a fossil represent?
a) Living organism
b) Extinct species
c) Mutations
d) Genetic similarity
Answer:
b) Extinct species
49. What is the purpose of genetic recombination?
a) Ensures identical offspring
b) Increases genetic diversity
c) Speeds up reproduction
d) Eliminates genetic mutations
Answer:
b) Increases genetic diversity
50. What is the term for organisms that link two evolutionary groups?
a) Connecting links
b) Analogous species
c) Fossil evidence
d) Vestigial links
Answer:
a) Connecting links
51. What process leads to the formation of new species?
a) Speciation
b) Translocation
c) Transcription
d) Natural selection
Answer:
a) Speciation
52. What is the term for structures with different functions but similar origins?
a) Homologous structures
b) Analogous structures
c) Vestigial structures
d) Genetic structures
Answer:
a) Homologous structures
53. Who discovered the process of protein synthesis?
a) François Jacob and Jacques Monod
b) Har Gobind Khorana
c) Charles Darwin
d) Walter Sutton
Answer:
a) François Jacob and Jacques Monod
54. What is the relationship between fossils and evolution?
a) Fossils prove that evolution does not occur
b) Fossils provide evidence of past species and changes
c) Fossils are unrelated to evolution
d) Fossils represent living organisms
Answer:
b) Fossils provide evidence of past species and changes
55. What does the term “genetic drift” refer to?
a) Gradual adaptation
b) Random changes in allele frequency
c) Directional selection
d) Gene recombination
Answer:
b) Random changes in allele frequency
56. Which phase of evolution is considered the beginning of life on Earth?
a) Formation of complex molecules
b) Evolution of reptiles
c) Appearance of mammals
d) Development of humans
Answer:
a) Formation of complex molecules
57. Which method is used to study early human evolution?
a) Palaeontology
b) Genetic engineering
c) Biochemistry
d) Psychology
Answer:
a) Palaeontology
58. How does natural selection work?
a) Organisms adapt to survive
b) All individuals reproduce equally
c) Genes mutate randomly
d) Survival is unrelated to traits
Answer:
a) Organisms adapt to survive
59. What is the function of mutation in evolution?
a) Creates genetic uniformity
b) Eliminates weak traits
c) Provides raw material for evolution
d) Stops genetic changes
Answer:
c) Provides raw material for evolution
60. Which theory explains the gradual development of life on Earth?
a) Theory of Evolution
b) Theory of Relativity
c) Carbon Dating Theory
d) Quantum Theory
Answer:
a) Theory of Evolution.
61. What type of genetic material is present in all living organisms except viruses?
a) RNA
b) DNA
c) Proteins
d) Lipids
Answer:
b) DNA
62. What is the primary purpose of transcription in cells?
a) To replicate DNA
b) To synthesize RNA from DNA
c) To synthesize proteins directly
d) To transfer RNA into ribosomes
Answer:
b) To synthesize RNA from DNA
63. Which evolutionary evidence compares similarities in bone structure?
a) Anatomical evidence
b) Morphological evidence
c) Embryological evidence
d) Genetic evidence
Answer:
a) Anatomical evidence
64. Which evidence supports the gradual evolution of vertebrates from invertebrates?
a) Fossils
b) Morphological similarities
c) Carbon dating
d) Connecting links
Answer:
d) Connecting links
65. What is the structural unit of heredity in living organisms?
a) Chromosome
b) Gene
c) Protein
d) Ribosome
Answer:
b) Gene
66. What is the main function of mRNA in protein synthesis?
a) Carrying amino acids to the ribosome
b) Decoding genetic instructions
c) Transmitting the genetic code from DNA
d) Producing energy for synthesis
Answer:
c) Transmitting the genetic code from DNA
67. What is the main role of fossils in studying evolution?
a) Establish the structure of modern organisms
b) Understand the diet of ancient organisms
c) Provide evidence for extinct organisms and evolutionary stages
d) Document environmental conditions of the past
Answer:
c) Provide evidence for extinct organisms and evolutionary stages
68. Which type of natural evidence supports the common origin of various vertebrates?
a) Similar embryonic development
b) Differences in DNA
c) Habitat overlap
d) Functional organs
Answer:
a) Similar embryonic development
69. Which method helps scientists determine the timeline of species evolution?
a) Natural selection
b) Fossil study
c) Genetic modification
d) Carbon dating
Answer:
d) Carbon dating
70. What is the major factor leading to speciation?
a) Random mutations
b) Geographical and reproductive isolation
c) Use of organs in different environments
d) Similar environmental conditions
Answer:
b) Geographical and reproductive isolation.
71. What is the shape of chromosomes when they are fully condensed?
a) Helical
b) X-shaped
c) Spherical
d) Linear
Answer:
b) X-shaped
72. Which scientist is associated with the discovery of paired chromosomes in cells?
a) Walter Sutton
b) Gregor Mendel
c) François Jacob
d) Har Gobind Khorana
Answer:
a) Walter Sutton
73. What is the term for unused or redundant structures in an organism?
a) Vestigial organs
b) Homologous organs
c) Analogous organs
d) Functional organs
Answer:
a) Vestigial organs
74. What type of reproduction increases genetic diversity?
a) Asexual reproduction
b) Binary fission
c) Sexual reproduction
d) Budding
Answer:
c) Sexual reproduction
75. Which scientist is known for coining the term “mutation”?
a) Hugo de Vries
b) Charles Darwin
c) Alfred Wallace
d) Gregor Mendel
Answer:
a) Hugo de Vries
76. What is the significance of triplet codons?
a) They store genetic information
b) They code for amino acids
c) They synthesize DNA
d) They replicate chromosomes
Answer:
b) They code for amino acids
77. What is the scientific study of genes and heredity called?
a) Genetics
b) Biology
c) Anthropology
d) Botany
Answer:
a) Genetics
78. Which organs provide evidence of evolution through their presence in both functional and non-functional forms?
a) Homologous organs
b) Vestigial organs
c) Analogous organs
d) Specialized organs
Answer:
b) Vestigial organs
79. What is the evolutionary significance of mutations?
a) Prevents natural selection
b) Increases the survival rate of species
c) Leads to genetic variation and new traits
d) Ensures genetic stability
Answer:
c) Leads to genetic variation and new traits
80. What term describes morphological similarities between related organisms?
a) Homologous structures
b) Analogous structures
c) Vestigial structures
d) Unique structures
Answer:
a) Homologous structures.
81. What role do fossils play in understanding human evolution?
a) They establish timelines and reveal extinct species
b) They prove Lamarck’s theory
c) They explain genetic mutations
d) They disprove evolution theories
Answer:
a) They establish timelines and reveal extinct species
82. Which molecule carries the genetic code for protein synthesis?
a) mRNA
b) tRNA
c) rRNA
d) DNA
Answer:
a) mRNA
83. What does the term “evolution” primarily refer to?
a) Sudden changes in an individual organism
b) Gradual development of species over time
c) Reproductive isolation
d) Extinction of species
Answer:
b) Gradual development of species over time
84. Which scientist disproved Lamarck’s theory?
a) Charles Darwin
b) Gregor Mendel
c) Hugo de Vries
d) Walter Sutton
Answer:
a) Charles Darwin
85. What is the basis of Darwin’s theory of natural selection?
a) Inheritance of acquired traits
b) Gradual accumulation of beneficial mutations
c) Direct intervention of environmental factors
d) Survival of organisms best adapted to their environment
Answer:
d) Survival of organisms best adapted to their environment
86. Which process ensures the diversity of traits in sexually reproducing organisms?
a) Mutation
b) Meiosis
c) Binary fission
d) Budding
Answer:
b) Meiosis
87. Which vestigial organ in humans is fully functional in other mammals?
a) Coccyx
b) Wisdom teeth
c) Appendix
d) Gall bladder
Answer:
c) Appendix
88. What term refers to structural similarities in embryos of different species?
a) Embryological evidence
b) Genetic similarities
c) Homologous structures
d) Analogous structures
Answer:
a) Embryological evidence
89. What is a connecting link between reptiles and mammals?
a) Platypus
b) Lungfish
c) Peripatus
d) Amphibians
Answer:
a) Platypus
90. Which theory focuses on the gradual accumulation of small genetic changes over time?
a) Evolutionary theory
b) Mutation theory
c) Theory of natural selection
d) Carbon dating theory
Answer:
c) Theory of natural selection.
91. What is the approximate time period for the evolution of modern humans?
a) 1,000 years ago
b) 50,000 years ago
c) 1 million years ago
d) 10 million years ago
Answer:
b) 50,000 years ago.
92. Which connecting link shows features of both annelids and arthropods?
a) Platypus
b) Peripatus
c) Lungfish
d) Amphioxus
Answer:
b) Peripatus.
93. What is the process called when two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material?
a) Crossing over
b) Mutation
c) Translocation
d) Speciation
Answer:
a) Crossing over.
94. What role does recombination play in evolution?
a) Maintains uniformity in traits
b) Prevents mutations
c) Increases genetic variation
d) Stops natural selection
Answer:
c) Increases genetic variation.
95. Which species is considered the first human-like ancestor?
a) Neanderthal
b) Cro-Magnon
c) Ramapithecus
d) Australopithecus
Answer:
c) Ramapithecus
96. What does the fossil record of Neanderthals suggest about their evolution?
a) They were directly related to modern humans
b) They were the first species to use fire
c) They were a separate branch of human evolution
d) They coexisted with dinosaurs
Answer:
c) They were a separate branch of human evolution
97. Which organelle plays a key role in the synthesis of proteins during translation?
a) Nucleus
b) Ribosome
c) Mitochondria
d) Chloroplast
Answer:
b) Ribosome
98. What is the evolutionary significance of vestigial organs?
a) They are fully functional in all species
b) They represent evolutionary remnants
c) They prevent genetic mutations
d) They are unique to humans
Answer:
b) They represent evolutionary remnants
99. What evidence did Charles Darwin use to support his theory of natural selection?
a) Fossils and geographical distribution of species
b) Genetic studies of DNA
c) Embryological similarities
d) Carbon dating techniques
Answer:
a) Fossils and geographical distribution of species
100. What is the process of gradual development of complex organisms from simpler ones called?
a) Mutation
b) Evolution
c) Transcription
d) Speciation
Answer:
b) Evolution
- COMPARISON OF ADJECTIVES
- Geography july 2025 – Download Answer sheet
- All the world’s a stage,And all the men and women merely players – Read the following poem and write an appreciation of it with the help of the given points in a paragraph format
- May he sit still, they said May the sins of your previous birth – Read the following extract and do the given activities
- One morning in a small apartment in Bombay a girl of about sixteen Read the following passage and do the activities
School Answer
SchoolAnswer.in